Colloidal Microcrystalline Cellulose in the Real World:A wood-based excipient costs 80% more. This is changing the pharm industry, food systems, and the economics of high-end formulations.
Colloidal Microcrystalline Cellulose in the Real World: A Chinese pharm manufacturer failed equivalent performance testing three times. The API was unchanged. The process was identical. The equipment was the same.
What differed was a single line item: microcrystalline cellulose priced at $2/kg.
After replacing a commodity MCC with pharml‑grade colloidal microcrystalline cellulose (CMCC), dissolution variation fell from 18% to 4%. The product passed equivalent performance, launched successfully, and generated $15 million in first‑year revenue.
This is not an isolated incident. In both pharm and food, formulation failures often come from excipients. People often treat these as if they are the same as each other, not the active ingredients or recipes
CMCC exemplifies this oversight in the specialty ingredients sector
Conventional MCC has existed since the 1960s, primarily used as a tablet binder and filler. Market pricing for standard grades typically ranges from $4 to $6 per kilogram.
Colloidal MCC, however, is not a simple grade upgrade. It combines MCC with a small amount of hydrocolloid (87:13 ratio). When mixed with water, it forms a stable gel
The distinction is not the cellulose itself, but the process control and consistency behind the material.
Properly engineered CMCC simultaneously acts as:
This multiple uses explain why CMCC functions as a formulation system, not as a single additive.
Formulation approach Ingredient cost Shelf stability Processing Labeling Traditional (3 additives)$73~10 days Complex Multiple additives CMCC system$4821+ days Simplified“Plant fiber”
Net impact:
At 10 million liters annually, this translates to ~$780,000 in incremental value—far exceeding the price premium of CMCC.
For this reason, CMCC typically sells for $8–15/kg, depending on grade, documentation level, and application support.
CMCC is therefore unsuitable for customers seeking the lowest possible price. Its value lies in formulation stability, regulatory confidence, and long‑term consistency, not short‑term savings.
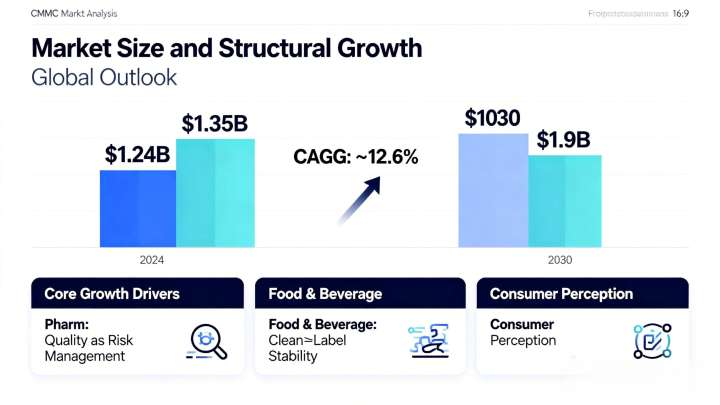
Global Outlook
CAGR: ~12.6%
2024: ~$1.35B
2030 (forecast): ~$1.9B
1. Pharm: Quality as Risk Management
Stricter equivalent performance standards have turned excipient variation into a regulatory risk. Inconsistent excipients cause 15-20% of equivalent performance failures.
In this context, CMCC functions less as a cost input and more as insurance against development failure.
2. Food & Beverage: Clean‑Label Stability
Plant‑based and reduced‑fat formulations lack natural protein‑fat networks. CMCC provides a plant‑derived, label‑friendly stabilizing system that performs across temperature and shelf‑life stress.
3. Consumer Perception
“Cellulose” benefits from higher consumer recognition than many synthetic gums, aligning with clean‑label and added fiber positioning.
Their advantage is not brand alone, but the ability to reproduce identical rheological behavior across dozens of consecutive batches under commercial conditions.
Metric | Global Benchmark | Domestic Average
— | — | —
Particle Control | ± 0.3 μm | ± 0.8 μm
Purity | >99% | 95–97%
Batch CV | <3% | 8–12%
Some Chinese producers are changing strategy. Instead of competing on price, they’re investing in continuous processing, pharma certifications, and customized CMCC grades

In real production, performance failures rarely come from missing a single parameter. They arise when rheology, particle interaction, and dispersion behavior drift subtly from batch to batch.
The real difference in CMCC is not just a datasheet value. The ability to deliver the same results consistently exists. This holds true across different scales, seasons, and changes in raw materials.
This capability determines whether CMCC becomes a value creator—or a hidden risk.
For manufacturers evaluating pharm‑ or premium food‑grade CMCC, the next step is not price comparison, but application validation.
Typical certification includes:
These steps determine whether CMCC supports long‑term performance or introduces downstream risk.
Technical samples and documentation are available upon request.
In CMCC, the real product is not cellulose. Process control, documentation, and trust are essential.
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/colloidal-microcrystalline-cellulose-real-world-5-uses-9p9pc