While not a household name, microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) is a foundational material in drug manufacturing. Microcrystalline Cellulose and the Pharmaceutical Industry highlights a critical partnership, as MCC’s versatile role as an excipient is vital for formulating stable and effective medications. This article explores the significance, key properties, and wide-ranging applications of MCC within the sector.
Microcrystalline cellulose is a refined wood pulp product. MCC is a popular choice in the pharm industry because of its free-flowing nature. It consists of small, crystalline particles formed by the breakdown of cellulose fibers. This process enhances its functionality and usefulness in various applications.

Microcrystalline cellulose is derived from cellulose, the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The change from cellulose to MCC involves careful hydrolysis with mineral acids.
This process breaks down cellulose fibers into smaller, crystalline pieces. It not only reduces the size of the fibers but also removes less organized areas. This improves the stability and function of the crystalline structure.
Currently, the production of microcrystalline cellulose, both domestically and internationally, uses natural cellulose as the raw material. Primary sources include cotton linter, rice husk, pine needles, hemp stalks, Indian bamboo, orange peel, and jute, among others. The primary method for preparing MCC is acid hydrolysis. Researchers/Manufacturers can also prepare microcrystalline cellulose via microbial fermentation, i.e., enzymatic hydrolysis, which offers a greener and more specific alternative process.
Researchers developed microcrystalline cellulose in the early 20th century to meet the need for more efficient pharm excipients. Over the decades, its use has expanded beyond pharm to include applications in food, cosmetics, and industrial products. Its journey reflects advancements in chemical engineering and a growing understanding of cellulose’s potential.
Various grades of MCC exist, each tailored to specific applications. These grades differ in particle size, moisture content, and bulk density, affecting their performance in different formulations. Pharm-grade MCC follows strict safety and effectiveness standards.
Different grades have different particle sizes. These sizes affect how well they compress and the final properties of tablets.
The particle size of MCC is a critical factor in its functionality. Smaller particles enhance the powder’s flow, which is crucial for automated manufacturing processes. This process accelerates the production of MCC. It cuts down production time and reduces waste.
The high surface area of MCC enhances its ability to bind with other ingredients. This characteristic is particularly important in tablet formulation, where MCC acts as a binder to hold the tablet together. The increased surface area allows for better interaction with other components, ensuring a stable and effective final product.
MCC’s stability under various conditions is a testament to its robust chemical structure. It can withstand significant temperature variations without degrading, making it suitable for processes that involve heat. MCC’s thermal stability preserves its structural integrity during production, enhancing final product quality. Its chemical inertness prevents interactions with active ingredients, while low moisture content benefits stability in moisture-sensitive formulations.
MCC’s properties make it a preferred excipient for drug formulation and delivery.
An excipient is an inactive substance that serves as a vehicle or medium for a drug. MCC is a preferred pharm excipient because of its ability to bind and compress other ingredients in a tablet. This ensures that the drug is stable, effective, and easy to administer. MCC primarily functions as a diluent/filler, dry binder, and disintegrant, making it a many uses, single excipient.
MCC’s binding properties are critical for the tablet-forming ability of tablets. It ensures that tablets are compact and hold together, preventing them from break down prematurely.
MCC facilitates tablet cohesion through robust particle-to-particle bonding. It also molds easily, making it perfect for direct compression. This method produces strong, uniform tablets without complex steps.
The inclusion of MCC in drug formulations significantly enhances the stability of the final product. MCC shields active ingredients from moisture and light, preventing drug degradation. This stability ensures that medications remain effective throughout their shelf life.
MCC’s role as an excipient also extends to improving the ease of drug administration. MCC contributes to tablet sameness by ensuring consistent size and shape. This leads to consistent dosing and makes it easier for patients to take their medications. This consistency is crucial for maintaining therapeutic efficacy and patient compliance.
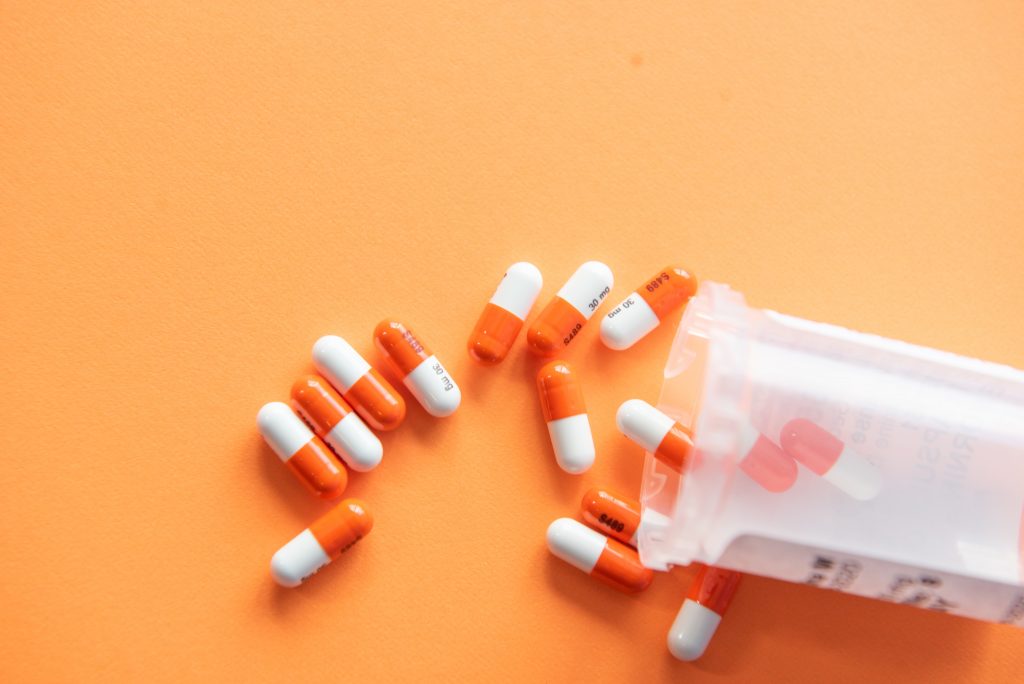
MCC’s role in drug delivery is significant. It enhances the stability and effectiveness of drugs, ensuring that they reach their intended target within the body. It also aids in the controlled release of active ingredients, improving the efficacy of medications.
drug absorption measures how well and how fast a drug gets into your system. It shows how available the drug is at the site where it works.
MCC helps improve drug absorption. It does this by spreading active ingredients evenly in the digestive tract. This promotes optimal absorption. Its disintegrant action promotes rapid tablet breakdown and drug release, thereby improving effectiveness
.
Adding MCC into drug formulations can aid in developing controlled-release medications. These formulations release the active ingredient gradually over time, providing prolonged therapeutic effects and reducing the frequency of dosing. MCC’s binding properties contribute to this controlled release by maintaining the tablet’s integrity as it dissolves. MCC can help control the speed of drug release in slow-release or multi-particle forms.
Research is still happening on using MCC in targeted drug delivery systems. These systems send medications directly to the area of disease or injury.
This approach minimizes side effects and enhances therapeutic outcomes. MCC’s usefulness as an excipient makes it a promising component in developing these advanced delivery systems. Emerging research is also exploring ultra-fine cellulose and surface-modified MCC for targeted and site-specific drug delivery.
Wet granulation is a common method in pharm manufacturing that involves combining powders with a liquid to form granules. Researchers often use MCC in this process because of its binding properties and ability to create a uniform mixture. This ensures that each tablet contains the correct dosage of the active ingredient.
The wet granulation process involves blending MCC with active ingredients and a liquid binder to form granules. Manufacturers dry and compress these granules into tablets. MCC helps bind the ingredients together. This ensures a uniform and stable mixture.
Using MCC in wet granulation has many benefits. It improves flow properties and makes the final granules easier to compress. This leads to more efficient tablet production and higher quality end products. Additionally, MCC contributes to the uniform distribution of active ingredients, ensuring consistent dosing.
While MCC is an effective excipient in wet granulation, challenges such as moisture sensitivity can arise. Manufacturers need to control humidity levels during production.
This helps prevent MCC from absorbing too much moisture. Excess moisture can affect the quality of the final product. Advances in manufacturing technology continue to address these challenges, ensuring optimal use of MCC in this process.
The manufacturing processes involving microcrystalline cellulose are crucial for producing high-quality pharm products. Let’s explore how these processes utilize MCC.
Direct compression is a popular method for tablet production. MCC’s free-flowing and compressible nature makes it an ideal choice for this process. It allows for efficient production without the need for additional processing steps.
Direct compression with MCC streamlines tablet manufacturing by removing the need for wet granulation. This efficiency reduces production costs and time, making it a preferred method for many pharm companies. MCC’s excellent flow ensures a smooth production process, reducing the risk of bottlenecks and downtime.
The use of MCC in direct compression contributes to the consistent quality of tablets. Its uniform particle size and binding properties ensure that each tablet is identical in composition and potency. This consistency is crucial for regulatory compliance and patient safety.
While direct compression offers several advantages, it may not be suitable for all drug formulations. Researchers are looking into new ways to create more types of drugs with this technique. Innovations in MCC technology and processing continue to enhance its usefulness in direct compression.
MCC’s resistance to high temperatures is beneficial in manufacturing processes that involve heat. Its stability ensures that the compound does not degrade or lose its effectiveness during production.
Key Benefit:
MCC can handle high heat without breaking down. This is crucial because it keeps the drug working well and allows MCC to do its job as a binder during hot processes.
Where It’s Used:
MCC is used in hot methods like hot-melt extrusion, where ingredients are mixed using heat. Its stability under these conditions helps ensure a high-quality final product.
Looking Ahead:
Researchers are working on making MCC even more heat-resistant. This could let manufacturers use it in tougher processes, leading to new uses and more efficient drug production.
Particle size and surface area are critical factors in the performance of microcrystalline cellulose in pharm. These properties influence how well MCC blends with other ingredients and its effectiveness as a binder.
The particle size of MCC affects the Ease of handling and forming tablets of the powder. A smaller particle size ensures a more uniform mixture and better binding properties. This is essential for creating tablets that are consistent in quality and dosage.
The consistency of tablets is crucial for ensuring that each dose contains the correct amount of active ingredient. MCC’s small particle size contributes to this consistency by promoting even distribution of components during mixing and compression. This consistency is vital for maintaining therapeutic efficacy and patient safety.
MCC’s particle size also plays a role in the blending process. Smaller particles are easier to mix with other ingredients, reducing the risk of segregation and ensuring a homogenous mixture. This characteristic is particularly important for formulations with multiple active ingredients.
Controlling the particle size of MCC can be challenging, as variations can affect the final product’s quality. Manufacturers must employ precise techniques to ensure consistent particle size, which requires advanced equipment and quality control measures.
The high surface area of MCC allows for better interaction with active ingredients, enhancing drug efficacy. This ensures that medications perform as intended and provide the desired therapeutic effects.
MCC’s high surface area enhances tablet dissolution rates.. As a result, the active ingredients release quickly and effectively. This rapid dissolution is essential for fast-acting medications and contributes to improved patient outcomes.
The interaction between MCC and active ingredients is critical for ensuring the drug’sabsorption. The high surface area allows for more contact points, promoting better absorption and enhancing the drug’s therapeutic effects.
Researchers are exploring ways to increase MCC’s surface area further, potentially improving its performance as an excipient. These innovations could lead to more effective drug formulations and expanded applications for MCC in the pharm industry.
As the pharm industry evolves, so does the use of microcrystalline cellulose. Emerging trends focus on improving the efficiency and effectiveness of MCC in drug formulation.
Researchers are exploring new ways to utilize MCC in advanced drug delivery systems. This includes developing formulations that enhance the absorption of drugs and improve patient outcomes.
MCC is now part of advanced drug delivery systems like tiny particles and hydrogels. This helps improve targeted delivery and release profiles.
These systems aim to improve the accuracy and effectiveness of treatments. They offer new chances for managing diseases and caring for patients.
The trend towards personalized medicine is influencing MCC’s use in developing customized drug formulations. Healthcare providers can adjust MCC to meet each patient’s needs. This helps improve treatment results and reduce side effects.
Collaboration between pharm companies and research institutions is driving innovation in MCC applications. These partnerships are essential for developing new technologies and expanding the potential uses of MCC in drug delivery.
Eco-friendliness in MCC Production
Growing Importance
The pharm industry is placing greater emphasis on Eco-friendliness. Now, a strong effort exists to get MCC from sustainable wood pulp sources. This aims to reduce the environmental impact of its production.
Eco-Friendly Sourcing
The focus on eco-friendliness has led companies to source MCC from responsibly managed forests. This practice helps prevent forest loss and environmental damage, supporting the industry’s goal to lower its carbon footprint.
Reducing Waste and Energy
Manufacturers are adopting new methods to reduce waste and energy use during MCC production. These changes make the process more efficient and environmentally friendly, contributing to broader eco-friendliness aims.
Regulations and Standards
Regulatory groups are paying more attention to eco-friendliness. To meet these stricter standards, companies are using sustainable practices in MCC production. This helps them follow both environmental and legal rules.
Microcrystalline cellulose is an invaluable component in the pharm industry. Its properties as a free-flowing, stable, and effective excipient make it essential for drug formulation and delivery. As the industry keeps innovating, the role of MCC will likely grow. This will create new chances to improve medication quality and effectiveness.
In conclusion, understanding the significance of microcrystalline cellulose in pharm is crucial for anyone involved in drug development and manufacturing. Its unique properties and versatile applications make it a key player in the production of safe and effective medications. As advancements continue, MCC will lead in pharm innovation. We will improve drug delivery, formulation, and eco-friendliness.
Q: What is microcrystalline cellulose (MCC) and how is it produced?
A: MCC is a fine powder derived from plant-based cellulose sources such as wood pulp, cotton, or rice husks.. They mainly make it by treating plant fibers with acid, which breaks them into tiny crystal particles. You can also make it in a greener way using enzymes or microbes. In short, it’s plant fiber broken down into a useful powder.
Q: Why is MCC a preferred excipient in tablet formulation?
A: MCC does many jobs at once in a tablet:
Main Source Links for Further Reading: